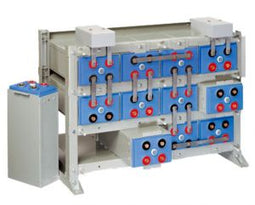
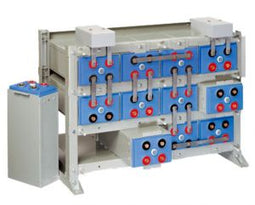
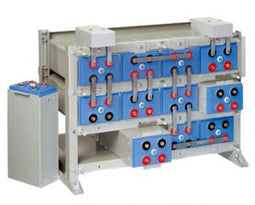
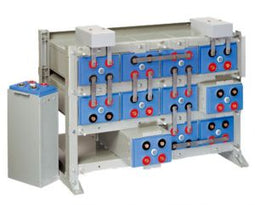
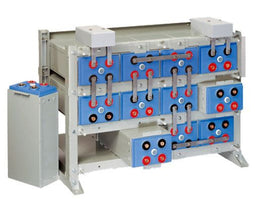
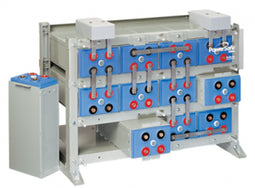
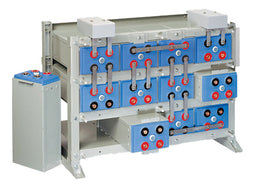
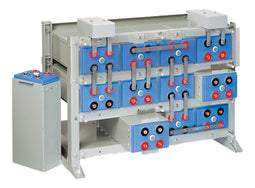
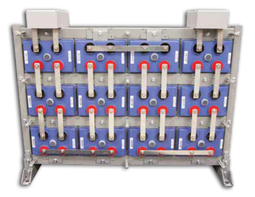
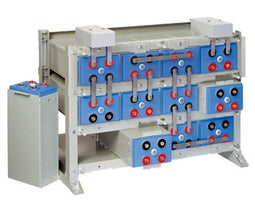
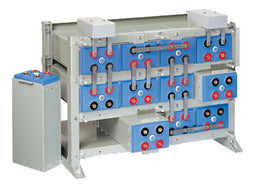
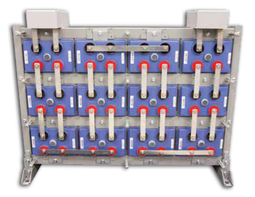
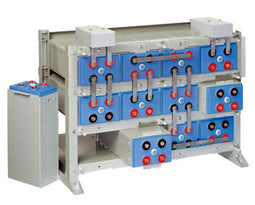
About AGM Batteries
AGM batteries are advanced versions of Lead-Acid batteries that are free from acid leakage and offer maintenance-free operation. AGM provides good electrical reliability and is lighter than the flooded lead-acid type. AGM has a very low internal resistance, and is capable of delivering high currents on demand.
Construction:
AGM batteries have electrolytes that grasp glass mats, as to restrict to freely flooding the plates. Fine glass fibers are interlace into a sheet to increase surface area enough to hold sufficient electrolyte on the cells. The glass-fibers that compose the fine glass mat do not absorb nor are they affected by the acidic electrolyte. These sheets are interlace out 2–5% after being soaked in acids, prior to manufacture completion and sealing. The plates in an AGM battery may be any shape. Some are flat, others are bent or rolled. AGM batteries, both deep cycle, and starting are built in a rectangular case to Battery Council International (BCI) battery code specifications.
Advantage:
- Zero Maintenance & Spill-proof through acid encapsulation in matting technology
- High specific power, low internal resistance, responsive to load
- Up to 5 times faster charge than with flooded technology
- Water retention (oxygen and hydrogen combine to produce water)
- Vibration resistance due to sandwich construction
- Stands up well to cold temperature
- Less prone to sulfation if not regularly topping charge
- Has less electrolyte and lead than the flooded version
Disadvantage:
- Slight Higher cost than flooded
- Sensitive to overcharging (AGM has tighter tolerances than gel)
- Capacity has gradual decline (gel has a performance dome)
- Low specific energy
- Must be stored in charged condition (less critical than flooded)
Comparison AGM Vs Lead Acid
|
AGM |
LEAD-ACID |
|
|
Cost |
Cost More than Lead-Acid |
Low-Cost |
|
Lifespan/Life cycle |
Lesser than Lead-Acid |
500 to 1000 cycle or 3-5 years |
|
Depth of Discharge |
Deep discharge capacity up to 80% |
Typically low discharge capacity, somewhere around 50%-65% |
|
Efficiency |
80% |
(80-85)% |
|
Charge Rate |
Up to 5 times higher than lead-acid |
Can’t charge fast due to overheating |
|
Energy Density |
Slightly Higher than Lead-acid battery |
Comparative more space required |

 Bifacial
Bifacial Mono Crystalline
Mono Crystalline Poly Crystalline
Poly Crystalline Thin Film
Thin Film Foldable Solar Panel
Foldable Solar Panel Residential On Grid
Residential On Grid Commercial On Grid
Commercial On Grid Solar Storage / Hybrid Inverter
Solar Storage / Hybrid Inverter Solar Battery Inverter
Solar Battery Inverter RV Off Grid Solar Inverter
RV Off Grid Solar Inverter Lithium ion Batteries
Lithium ion Batteries AGM Batteries
AGM Batteries Lead Acid Batteries
Lead Acid Batteries Lithium Batteries
Lithium Batteries Lead Carbon Batteries
Lead Carbon Batteries Deep Cycle Flooded Battery
Deep Cycle Flooded Battery Solar Workstation
Solar Workstation Solar Security Camera
Solar Security Camera Solar Freezer
Solar Freezer Battery Charger
Battery Charger Meters
Meters Distribution Panel
Distribution Panel Battery
Battery Invertor Charger
Invertor Charger Breaker Panel
Breaker Panel