Collection: Bifacial
Type
Manufacturer
Wattage
Technology
Frame Material
Max System Voltage
Module Connector
Inverter Sub Category
Solar Inverter Phase
Inverter Capacity (in KW)
Inverter Type
AC Frequency
Compatible Battery Voltage
Maximum DC Input Voltage
Number Of Cells
Cell Type
Battery Technology
Capacity Range (kWh)
Controller Type
Controller Capacity (Amps)
Color Temperature
Input Voltage
Mounting
Lumens
Approvals / Ratings
Collection: Bifacial
- Previous
- Next
About Bifacial
Bifacial solar modules offer many advantages over traditional solar panels. Power can be produced from both sides of a bifacial solar module, increasing total energy generation. They’re often more durable because both sides are UV resistant, and potential-induced degradation (PID) concerns are reduced when the bifacial module is frameless. Balance of system (BOS) costs are also reduced when more power can be generated from bifacial modules in a smaller array footprint.
If you knew there was a solar panel system for your home that delivered up to 50% more solar power compared to conventional solar panels, would you be interested? Then look no further than bifacial solar panels.
A bifacial solar panel is a double-sided energy factory that transform sunlight into electrical energy on both its top and bottom sides.
Bifacials are equipped with solar cells on both the top and the rear of the panel. They are usually monocrystalline, although polycrystalline can be used. Because they are slim, they resemble thin-film solar panels. Bifacial solar panels are frequently frameless, too.
The top of each solar module is covered in protective glass. The flipside may be glass or a clear back sheet. This is different from conventional solar panel systems with opaque backings.
Here’s a summary table that illustrates the differences in solar cell efficiencies between the major commercial options.
|
Type of Solar Panel |
Total Solar Cell Efficiency |
|
18% + |
|
|
15–17% |
|
|
11–15% |
|
|
Bifacial Monocrystalline |
20% + |

 Bifacial
Bifacial Mono Crystalline
Mono Crystalline Poly Crystalline
Poly Crystalline Thin Film
Thin Film Foldable Solar Panel
Foldable Solar Panel Residential On Grid
Residential On Grid Commercial On Grid
Commercial On Grid Solar Storage / Hybrid Inverter
Solar Storage / Hybrid Inverter Solar Battery Inverter
Solar Battery Inverter RV Off Grid Solar Inverter
RV Off Grid Solar Inverter Lithium ion Batteries
Lithium ion Batteries AGM Batteries
AGM Batteries Lead Acid Batteries
Lead Acid Batteries Lithium Batteries
Lithium Batteries Lead Carbon Batteries
Lead Carbon Batteries Deep Cycle Flooded Battery
Deep Cycle Flooded Battery Solar Workstation
Solar Workstation Solar Security Camera
Solar Security Camera Solar Freezer
Solar Freezer Battery Charger
Battery Charger Meters
Meters Distribution Panel
Distribution Panel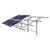 Battery
Battery Invertor Charger
Invertor Charger Breaker Panel
Breaker Panel









